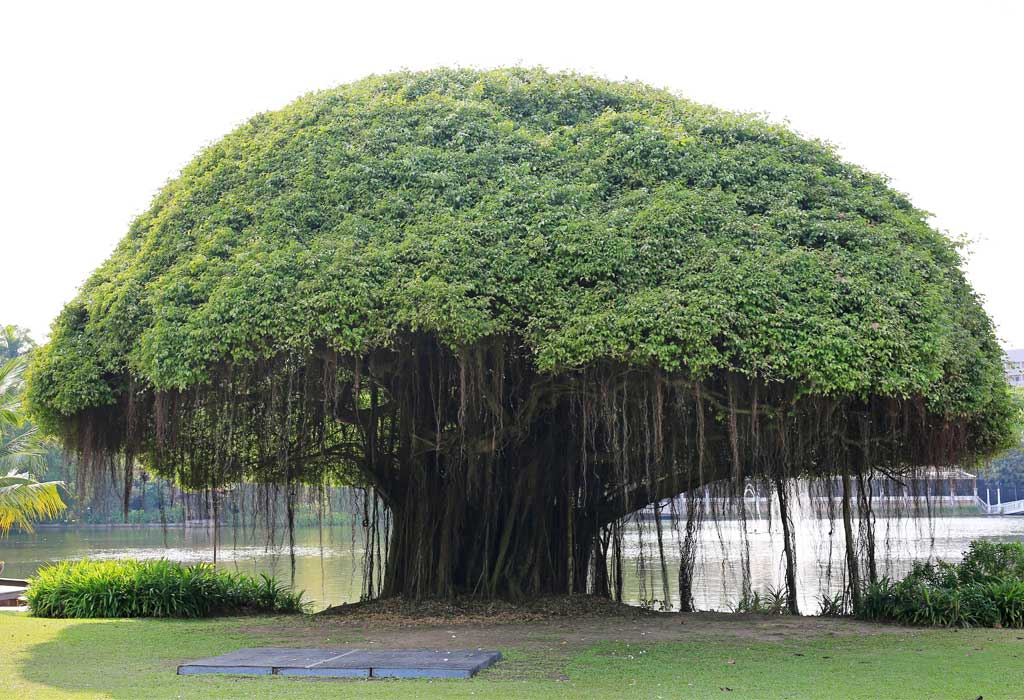
The Great Banyan Tree (Ficus Benghalensis) – The National Tree of India
The Great Banyan, India’s National Tree – The banyan tree, which has unusual hanging roots and excellent medicinal qualities, is the national tree of India. This tree has cultural, mythological, and religious importance in India. Banyan trees are typically situated in the middle of villages, the site of “panchayat” meetings. The banyan tree, which is regarded as India’s national tree, represents power and unity. (Ficus Benghalensis Tree)
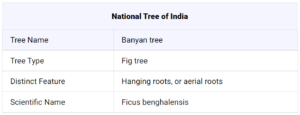
Ficus Benghalensis is the scientific name for the banyan tree, and its outwards extending branches serve as its major means of identification. Learn more about India’s national tree, including its features, origins, and myths around it.
National Tree of India – Overview
The banyan tree is a type of fig tree classified by its outward-growing roots. These roots are also known as adventitious prop roots or aerial roots. India’s national tree, the banyan tree, has great cultural significance there. A quick overview of banyan trees can be seen below.
How Does the Indian National Tree Grow?
The banyan tree, which is our national tree, develops from accidental prop roots. In simpler terms, it means that every banyan tree begins its life by developing on another plant. Following germination, a new banyan tree’s trunk appears from a crack or crevice on the hanging root of a developed host tree. This growing tree gradually begins to grow its own aerial roots.
Banyan trees are able to develop in clusters, with many trunks supporting the roots. When combined, they can create a picture of a forest covering a large area of the land. India rightly regards the banyan tree as its national symbol since it represents strength and unity.
National Tree – Features
Banyan trees have several unique features that help them stand out from other trees. One of their unique characteristics is their “hanging roots.” Here’s a quick overview of their other features:
- Starting life as an epiphyte, or a plant that grows on another host plant.
- Aerial roots grow outwardly rather than underground.
- Indefinite growth.
- Large and glossy leaves.
National Tree – Scientific Information
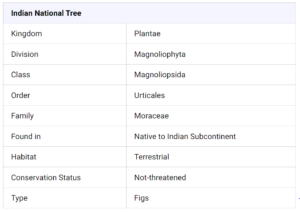
This table shows the scientific classification, status, and size of the national tree of India (banyan tree) –
Indian National Tree – Cultural Significance
The banyan tree, India’s national tree, is extremely important to the country’s culture. In rural India, the banyan tree is a vital part of local culture. It is the site of village panchayats. People frequently sit in the tree’s shade for relief from the scorching summers of the countryside. The national tree is revered in the hopes of bringing prosperity, growth, and wealth.
The Mythical and Spiritual Significance of Banyan Tree
The national tree of India has various mythological and spiritual importance. In Hinduism, the Bargad (Banyan) tree is known as ‘Ashwath Vriksha.’ Here are some reasons for its mythical and spiritual significance:
- It is considered immortal and an essential component of Indian mythology and legends.
- It is also the sign of the legendary ‘Kalpa Vriksha’, or ‘Tree of Wish Fulfillment.
- It shows eternity with its constantly expanding branches.
- It is also referred to as the tree of God, which grants wishes.
- In ancient Indian history and Hindu mythology, the banyan tree symbolizes the Almighty and longevity.
In addition, the tree is believed to grant wishes and provide material blessings.
Benefits of the National Tree of India.
There are a number of benefits related with our national tree:
- Its fruits are delicious and nutritious, and they can reduce skin irritation and swelling.
- The bark and leaf extracts are used to stop bleeding.
- Cleaning your teeth with aerial roots improves gum and tooth health. Leaf bud infusion is used to treat chronic diarrhea and dysentery.
- The Banyan tree is known for producing shellac, which is used as a surface abrasive and glue. It is mostly created by lac-producing insects that live in banyan trees.
- The milky white sap is used to polish metals like brass and copper.
FAQs
Q.1 Which is the national tree of India?
The banyan is India’s national tree. This tree is known by the scientific name Ficus benghalensis. In India, it is valued for both its medical benefits and religious importance. The prominent feature of this tree is its hanging roots.
Q2. Why is the Banyan tree known as India’s national tree?
The banyan tree is considered India’s national tree due to its religious, mythical, and cultural significance. It is considered precious in Hinduism and even worshipped. It is also known as the national tree, as it represents strength and unity.
Q3. What is the scientific name of India’s national tree?
The banyan tree, India’s national tree, is known scientifically as Ficus benghalensis. The banyan tree is a fig tree with adventitious or hanging roots. In Hindi, the Banyan tree is known as the ‘Bargad’ tree, and it is also known as the Indian fig.
Q4. Is Peepul the national tree of India?
The Peepul tree has cultural and religious significance, however it is not India’s national tree. The banyan tree is India’s national tree. These trees can be found across the country, regardless of climate or geography.
Q5. What are the Banyan tree’s benefits?
Our national tree offers various advantages, including delicious fruits that heal skin irritation and swelling, leaf extracts that stop bleeding, white sap that is used to polish metals such as brass and copper, and aerial roots that may be used to clean teeth to avoid gum and tooth issues.
Also Read :
